Uncover the Key Differences Between Additive Manufacturing and CNC Machining: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to creating a new part, there are two standard manufacturing methods: CNC machining (Subtractive manufacturing) and 3D printing (Additive manufacturing). With time, both methods have evolved to meet different demands. Therefore, it becomes crucial to understand their suitability as per your requirement.
This article discusses CNC and 3D printing machining and the difference between the two methods.
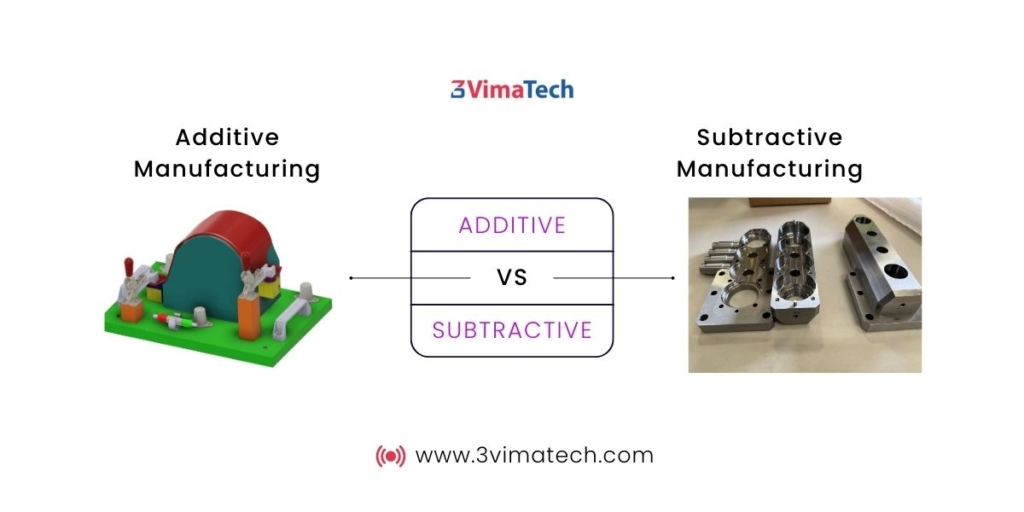
Subtractive Manufacturing vs Additive Manufacturing
3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing, while CNC machining is subtractive manufacturing. The CNC machine starts with a block of material known as Blank and creates a finished product by cutting away the material. The object is shaped by using cutters and spinning equipment.
The CNC machine has great dimensional accuracy and various compatible materials such as metals, wood, and plastics.
3D printing (additive manufacturing) creates parts layer-by-layer. It uses plastic filaments (FDM) and resins (SLA/DLP). The layers of these materials are solidified using energy sources like a laser or heated extruder to form the finished product.
3D printing gives the freedom to shape, accuracy, speed and ability to cut costs and weight in parts.
Difference between Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) and Subtractive manufacturing (CNC machining)
CNC machining and 3D printing satisfy different demands and provide various advantages.
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing machining) | Subtractive Manufacturing (CNC machining) |
| Creates parts by adding material layers | Creates parts by removing material layers |
| Slow process, better for smaller parts | Better for larger parts |
| Rough finish that needs further post-operational polishing | Surface finish that is more defined and requires less postoperative finishing |
| Less precise part tolerances | Able to hold extremely precise part tolerances |
| Less costly material costs | More expensive material costs |
| Produce less material waste | Produce more material waste |
| Intricate details easier to create | Complicated software and other capabilities may be needed for intricate details (5 axis) |
| 3D printers can work only with limited materials using metals, plastics and polymers. They can’t work with metals that have high melting points. | CNC Machining can work with various materials such as wood, metal alloys, acrylics, modelling foam and thermoplastics. |
Similarities Between Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) and Subtractive Manufacturing (CNC)
Despite the differences, CNC machining and 3D printing have some things in common:
- Both make 3D products based on 3D models
- Both follow instructions from the computer
- Both are compatible with STL and OBJ file types.
Which is Better for Prototyping?
CNC machining can be a little more costly and is typically reserved for production. However, CNC machining requires a more hands-on approach because of setup time and operator oversight.
But if you have the equipment, subtractive manufacturing is viable due to its precision and build tolerance. Although it’s a great piece of equipment, the cost or setup time can make it seem overkill.
3D printing is specifically designed for rapid prototyping. Additive manufacturing has the edge over subtractive when it comes to design and cost-efficiency requirements.
When it comes to revisions, the cost is significantly less as compared to subtractive manufacturing.
Overview of 3D Printing
Hideo Kodama of the Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute created the first 3D printing production machinery when he made two additive techniques for creating 3D models.
Stereolithography, melting, and sintering are the three basic types of 3D printing processes:
Sintering is a process that uses heat to create high-resolution objects without melting the material.
Metal powder is used for direct metal laser sintering, whereas thermoplastic powders are used for selective laser sintering.
Powder bed fusion, electron beam melting, and direct energy deposition are three 3D printing processes that use high-temperature melting to create objects by melting the components together.
Photopolymerization is used in stereolithography to create parts. This technique specifically interacts with the material to cure and solidify a cross-section of the product in small layers using the proper light source.
Overview of CNC Machining (Subtractive Manufacturing)

When a CNC system is turned on, the software is programmed with the necessary cuts. It sends them to the relevant tools and machinery, which perform the required dimensional tasks like a robot.
The code generator within the numerical system in CNC programming typically considers mechanisms as faultless, even though there is a potential for errors when a CNC machine is commanded to cut in more than one direction simultaneously.
The component programme, a set of inputs, specifies where a tool should be placed in a numerical control system. Programs are entered into numerical control machines using punch cards.
Contrarily, tiny keyboards are used to input CNC machine codes into computers. A computer’s memory is where CNC programming is stored. The actual code is written and edited by programmers.
As a result, CNC systems have far greater processing capacity. The best part is that CNC systems are far from static because updated programmes may be added to older ones by modifying the code.
Conclusion
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized the way products are manufactured. From production times to greater design flexibility, from cost reduction to waste reduction, there are various advantages to using additive manufacturing processes.
When it comes to using subtractive manufacturing processes, it is best suited for creating products made from various metals, woods, ceramics, and foams. It helps produce highly refined products that can withstand long-term and high-stress usage.
In short, additive technologies are more appropriate for small components and complicated or very complex designs. In contrast, subtractive procedures become more competitive when later stages of the development process call for larger batches.
Frequently Asked Questions
CNC machines, robots, 3D printers, laser cutters, waterjet cutters, and ultrasonic welders are a few examples of advanced manufacturing equipment.
Metals, plastics, wood, ceramics, and composites are commonly used with a CNC 3D printer.
Some of the most popular subtractive manufacturing techniques are CNC machining, milling, turning, and drilling.